- Serious digoxin toxicity can cause hyperkalemia; administration of potassium supplements in these patients may be hazardous. After treatment with DIGIFab, serum potassium concentration may decrease rapidly and must be monitored frequently, especially during the first several hours after administration.
- The clinical condition of patients with poor cardiac function may deteriorate secondary to the withdrawal of the inotropic action of digoxin by DIGIFab. If needed, additional support can be provided by using other intravenous inotropes such as dopamine, dobutamine, or vasodilators.
- Care must be taken not to aggravate digoxin-induced rhythm disturbances. Restoration of digoxin therapy should be postponed, if possible, until Fab fragments have been eliminated from the body, which may require several days; patients with impaired renal function may require 1 week or longer.
Preparation and
Administration of DIGIFab1
DIGIFab Use and Storage
- Each vial of DIGIFab contains 40 mg of digoxin immune Fab protein and is intended for one-time use only.
- The reconstituted product should be used promptly. If not used immediately,
store under refrigeration at 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F) for up to 4 hours.
Reconstitution

Reconstitute each vial of DIGIFab with 4 mL Sterile Water for Injection USP.

Gently mix to obtain a solution containing approximately 10 mg/mL digoxin immune Fab protein.
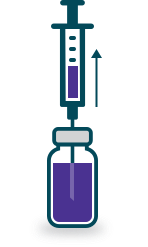
Add the reconstituted product to an appropriate volume of 0.9% sodium chloride for injection.

Infants and Small Children
- For infants and small children who may require very small doses, reconstitute the 40 mg as directed and administer undiluted using a tuberculin syringe.
- For very small doses, dilute a reconstituted vial with an additional 36 mL of isotonic saline to achieve a concentration of 1 mg/mL.
Infusion
Administer slowly as an intravenous infusion over at least 30 minutes. If infusion rate–related reactions occur (eg, hypotension, wheezing, urticaria), the infusion should be stopped and restarted at a slower rate.
If cardiac arrest is imminent, DIGIFab can be given by bolus injection. With bolus injection, an increased incidence of infusion-related reactions may be expected.

